To overcome your competitors in the SERP, get more traffic, conversions, and more leads, you should first study your competitors thoroughly. This way, you can figure out the strengths and weaknesses in their SEO strategies and draw up your own action plan, taking into account the current market state in your niche.
Read below what a complete SEO competitor research consists of and how to perform it with modern tools.

Money vector created by iwat1929 – www.freepik.com
What is a competitive analysis?
Competitor analysis in SEO is a detailed study of different aspects of the state of your competitors’ sites. The competent analysis involves checking your competitors’ positions in search results, their traffic, CTR, top pages in the SERP, keywords that work best for them, domain trust, backlinks, and much more with the help of professional tools.
Who must do competitor research?
Whether you choose a niche for your new business or determine a new business direction, you need a thorough analysis of potential competitors. If you already have a business but are not 100% happy with the results or want to rethink pricing, marketing, etc., you need competitor analysis. So, actually, competitor analysis should be held by small business owners, founders, and company managers, as well as marketers and SEOs.
Why do you need competitor monitoring?
Competitor analysis helps to promote a product on the market effectively. Competitive analysis shows:
- who is your real competitor in the fight for the client;
- what strategy your competitors are using;
- how your competitors are doing;
- what are the main sources of their website traffic;
- how your competitors are using advertising tools and what their budgets are;
- which direction you should develop to increase market coverage and profits;
- how to separate yourself from competitors and find your advantage;
- how to show the uniqueness of the product and attract an additional target audience.
By knowing everything about your competitors and their online promotion efforts, you can craft your own strategy and make it more successful.
What does a SEO competitor analysis consist of?
While doing competitor research, you analyze the following data:
- Organic traffic;
- Ranking changes;
- Organic keywords (top-performing, new, and lost);
- Top pages in organic search with traffic share;
- Semantics comparison;
- Paid traffic volume and total traffic cost;
- Keywords for paid advertising;
- Top pages in paid search;
- Domain and page trust;
- A number of backlinks and referring domains, etc.
It looks like a bunch of metrics, doesn’t it? Fortunately, professional tools allow you to analyze your competitors’ SEO performance in just a few clicks. One of these tools is SE Ranking. It has a multifunctional and easy-to-use competitor research tool that both SEO specialists and business owners can use to check other websites’ traffic, keywords, paid campaigns, and much more. Therefore, below we will show all the stages of deep competitive research with examples from this service.
So let’s move on to our step-by-step guide to in-depth competitor analysis.
Step 1. Identify your competitors
So, the first thing you need to do is identify your competitors. Sometimes these are far from the companies that come to your mind first. Actually, all competitors can be divided into three groups:
- Direct competitors are directly vying for your clients.
- Potential competitors sell the same goods or services and target the same types of customers but don’t work in your market area for now. For example, if you sell books in New York, a bookstore in Washington will be your potential competitor.
- Indirect competitors are businesses in the same category, but their goods or services are different. For example, you sell non-fiction books, and your indirect competitor sells children’s books.
Think of this list when collecting competitors. Also, pay attention to scale, marketing budget, and traffic when making up a list of your competitors. They should be more or less close to you in terms of these parameters.
But how do you find your competitors? You can start with the SE Ranking tool we’ve already mentioned. Its competitor research tool automatically generates a list of organic competitors based on the keywords they use and their traffic volume. Some of them may be your direct competitors.
Also, the tool can show paid competitors – those who run Google Ads. Actually, the competitive research report is divided into two large parts – organic and paid ones.
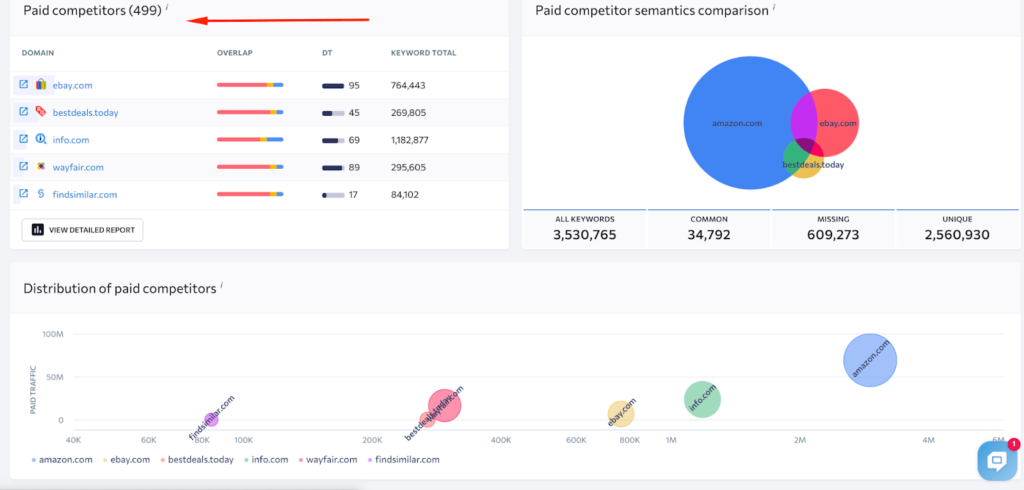
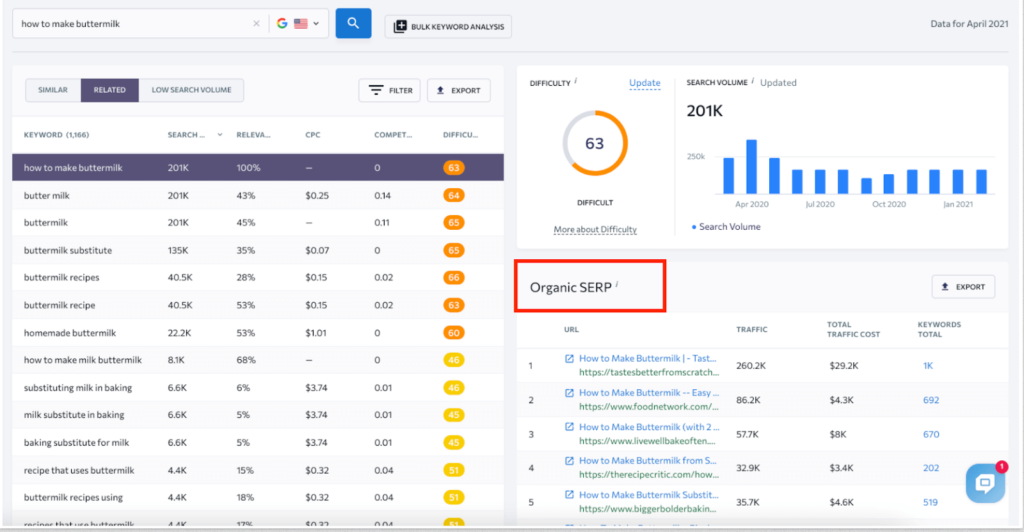
If you don’t have a website yet but want to understand who your competitors are, you can use another module of SE Ranking called the Keyword Research tool. Enter your seed keyword there (for example, “coffee shop in Austin”), and you’ll see the top 100 pages from the SERP for this query, as well as other related and similar keywords and search volume for each of them.
This very tool will also help you find your direct competitors based on target keywords. Just make them more geo-specific and think of commercial intents when searching for competitors using specific queries. If you type just an informational query, most likely, you’ll see articles and informational sites – and that’s not what you’re looking for.
So, as the result of step 1, you need to make up a list of your competitors you will analyze more closely in the next stages.
Step 2. Make a traffic breakdown
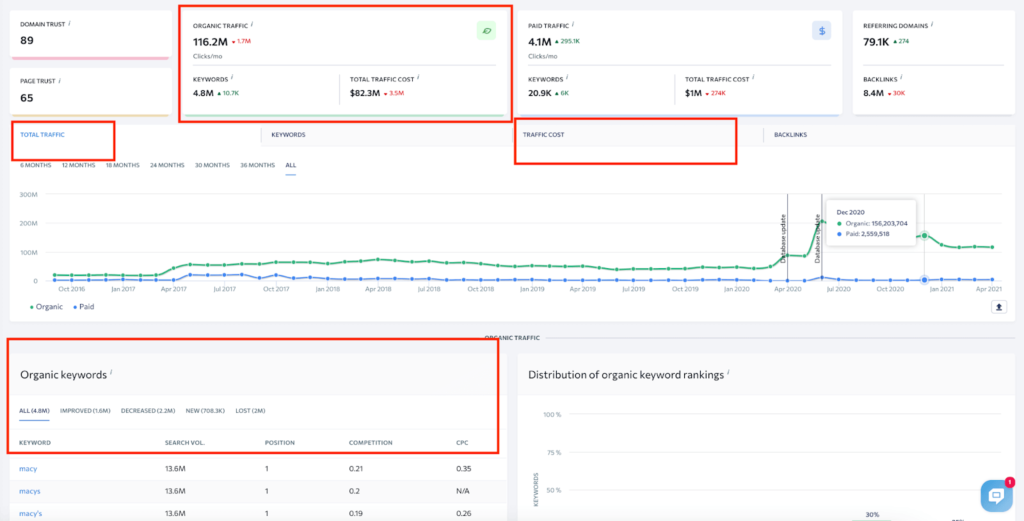
Now that you have a list of competitors, it’s time to examine their SEO efforts thoroughly. Let’s start with traffic because this metric indicates the volume of the audience and potential customers of the brand. Here’s what you should study for each competitor using the different sections of the SE Ranking competitor research tool:
- Traffic estimate. Analyze the traffic volume on the site in recent months and pay attention to where the traffic fluctuations were and analyze what changes were happening to the site at that time.
- Traffic sources. It may be organic (driven by SEO), referral, paid, and direct. Plus, some users come to your site from email marketing campaigns and social. Pay special attention to sites with the biggest share of organic traffic – these are actually good at SEO. You can get more ideas on keyword usage from them.
- Traffic cost. If businesses are promoting through Google Ads, you will see the cost per click as well as the volume of traffic for each page that is being promoted through paid ads. By analyzing this metric, you can better plan your own paid advertising costs.
- Keywords driving traffic to a website. Research the top keywords that your competitors are getting the most traffic for. In the Competitive Research tool by SE Ranking, you can find this data in the Organic Keywords and Paid Keywords sections.
Step 3. Spy on competitors’ organic keywords
Let’s now dive deeper into competitors’ organic keywords. Your task is to scrutinize the keywords generating the most traffic for your competitors, as if they work well for them, they may work well for you.
You can use the Ranking Changes section in the Competitive Research tool to track new, lost, improved, and decreased keywords used by your competitors. You will see the full info on their rankings, search volume, traffic estimate, CPC, and search results overview by country.
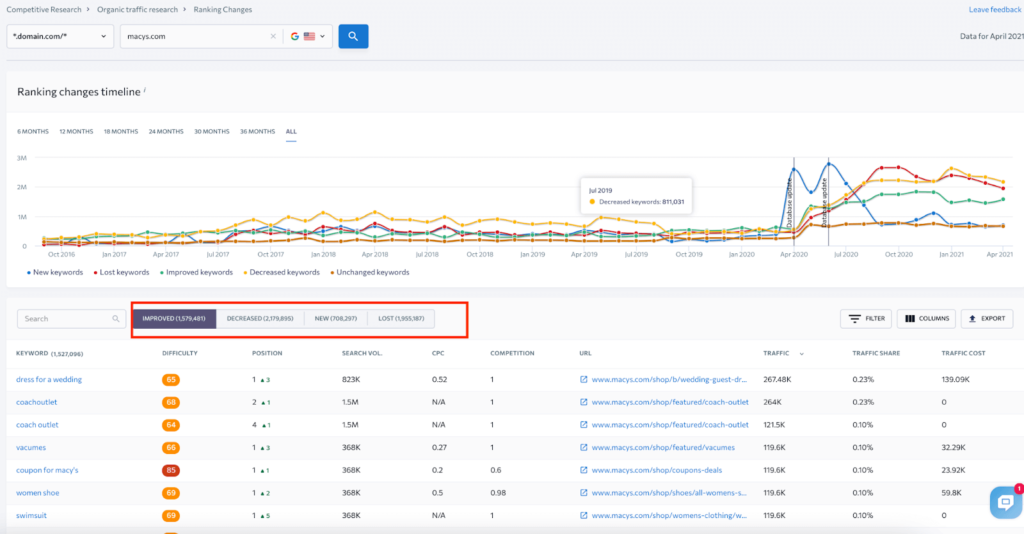
There is really a lot of information, and you can click on every keyword your competitors are using to see the top 100 pages for that keyword as well as all the basic metrics. So you can get an impression of which keywords work best for your competitors, which ones work worst, and for which queries the competition is too high, and the SERP is already clogged with large brands and aggregators.
Step 4. Find content gaps
By analyzing the keywords of your rivals, you can get more ideas for your own semantic core, as well as compare the keywords that you and your competitors use. Plus, you can spot some missed keywords other your competitors already use successfully.
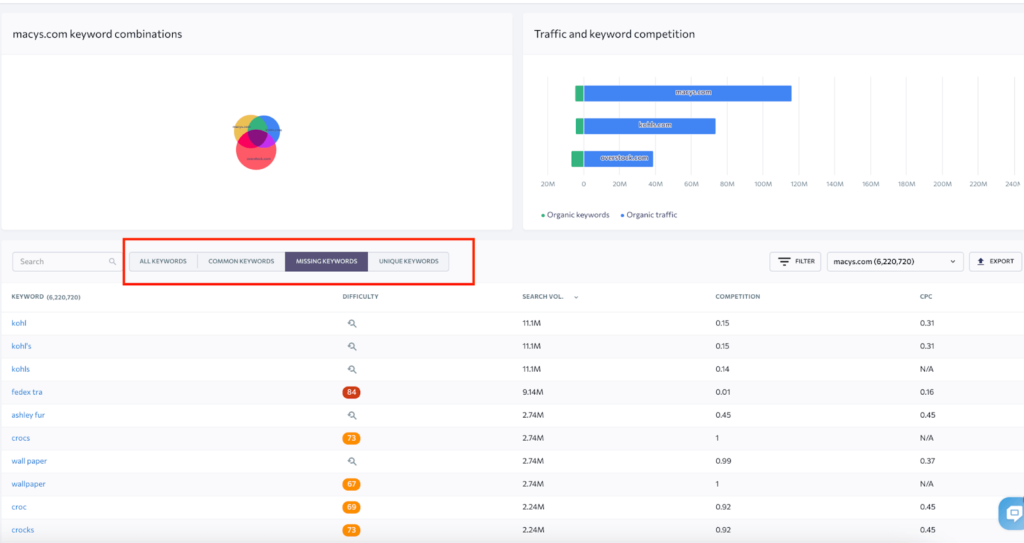
To do such research in the Competitor Research tool, go to the Competitor comparison subtab, take two competitors plus your site, and compare the semantics.
- The “Common” tab will show the keywords all of you use.
- The “Missing keywords” tab will show you the queries both of your competitors use, but you don’t.
You can sort all the keywords from these tabs by their search volume, CPC, level of competition, and the total number of pages present in the SERP. That will help you to analyze these queries and decide whether they are relevant for you or not.
Step 5. Use content opportunities
When you analyze your competitors’ content, you can find out what topics they cover and what they miss, so you can surpass them by writing an interesting piece of content on the topic that your competitors have not yet covered.
Plus, by examining your competitors’ top pages in the SERP, you can figure out which of their articles rank high for which keywords. It may be a good start for you to write an article on the same “hot” topic with the same keywords but make it even more interesting, longer, and better-structured.
You can use SE Ranking’s Keyword Research tool to see who is on top of the search for any keyword and examine their top pages, especially those from their blogs. Then analyze those pages for keywords and the length of the article, and so you get a ready technical assignment for your SEO copywriter!
 Step 6. Track backlink profile history
Step 6. Track backlink profile history
Backlinks remain an important component when ranking your website in 2021. The trick is to get backlinks only from reliable sources with high domain trust. Searching for such sites to place backlinks can be very long and exhausting, so you can spy on competitors to find out which sites link to them and negotiate with these resources. Actually, if you have a list of sites your competitors get backlinks from, you don’t need to search for donors on your own – your rivals have already done most of the work.
Still, there are some points you should pay attention to:
- Quality of those backlinks. Sites get many backlinks from different resources, but not all of them may be considered good. The main SEO metric here is domain trust. The donor is usually considered to be weak with a domain trust less than 40. It can indicate low-quality backlinks, or, on the other hand, it’s a young website that still works on its domain trust. Therefore, if you want to analyze potential competitors (newcomers), look through the website backlink profile manually to evaluate how the particular competitor grows its backlink profile.
- Nofollow vs. dofollow backlinks. Usually, nofollow tags are used for paid backlinks, and their only benefit is that they can bring potential customers (traffic) and increase brand awareness. When examining donors, your competitors get backlinks from, pay special attention to those that post links without the “nofollow” tag.
- Backlink gaps. Comparing your competitors’ backlink profiles with yours, you may notice that all of them get links from the site example.com and you don’t. That’s the opportunity you’re missing since this site is definitely collaborating with businesses like yours.
To get full information on your competitors’ backlink profiles, go to the Backlink Checker tool in SE Ranking. It analyzed the links from every possible angle. Simply enter your competitor’s website address, and you’ll get full info on these metrics:
- Domain trust;
- Page trust;
- Number of referring domains;
- Dofollow and nofollow ratio;
- Top referring domain anchors;
- Top backlink anchors;
- Sponsored backlinks;
- New and lost backlinks, etc.
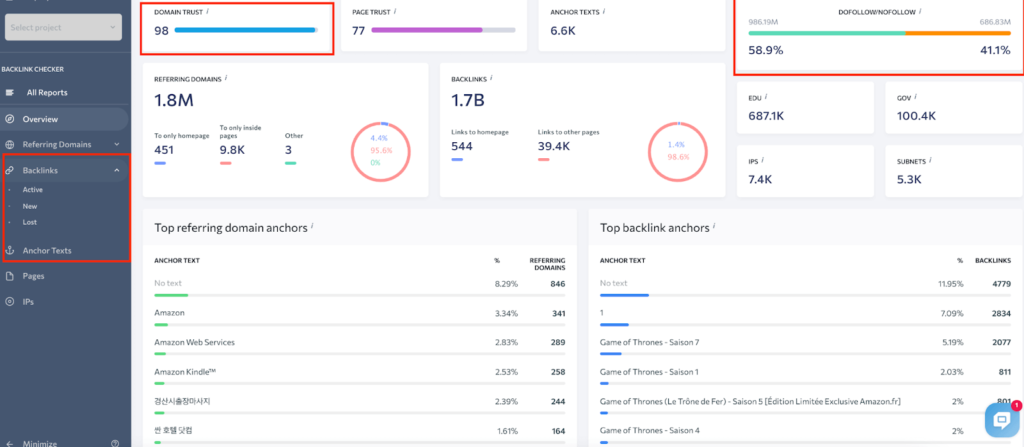
While you’re analyzing your competitors’ backlinks, try to figure out their strategy. Pay attention to how often they get new backlinks and what the domain trust of their donors is. Determine for yourself the sites from which competitors receive the most backlinks and which anchors are used. Download their best backlinks to create your own backlink strategy and make it more effective.
Step 7. Examine the page structure & UX
UX and page structure play a great role in rankings since they refer to behavioral factors. Comparing similar pages of your competitors will help you understand some individual issues that make your competitors rank higher than you. It will also serve you well if you’re just developing your site structure and design and want to make it even better. Here are some areas to pay special attention to in term of page structure:
- Titles and meta descriptions. These two make up the snippet that is shown in the search results. Analyze the keywords your competitors use in their titles and descriptions, as well as their length and engagement.
- H1s and other subheadings. Google loves well-structured pages, so pay attention to how your competitors format the page and text on it, how many levels of subheadings they use, and whether they use keywords in them.
- Breadcrumbs. A breadcrumb trail is a part of the navigation scheme that shows the users where they are now exactly and the pages’ hierarchy. Breadcrumbs ease the navigation both for users and are beneficial for SEO since they decrease the bounce rate. So pay attention to whether your competitors use breadcrumbs and how they look like.
- URL structure. Pay attention to the nesting levels of URLs and whether your competitors use friendly URLs instead of hard-to-understand combinations of letters, numbers, and dashes.
As for UX, examine the site navigation and overall architecture. Test your competitors’ website load speed, and mobile responsiveness – these factors become more and more important for SEO, especially in the light of the upcoming Page Experience update.
Use SE Ranking On-Page Checker to check how well a web page is optimized for a certain query. You will see details on the title, meta description, URL structure, keyword density, the total number of keywords and top queries, and much more. That will help you work better on your similar pages and avoid mistakes your competitors may have made.
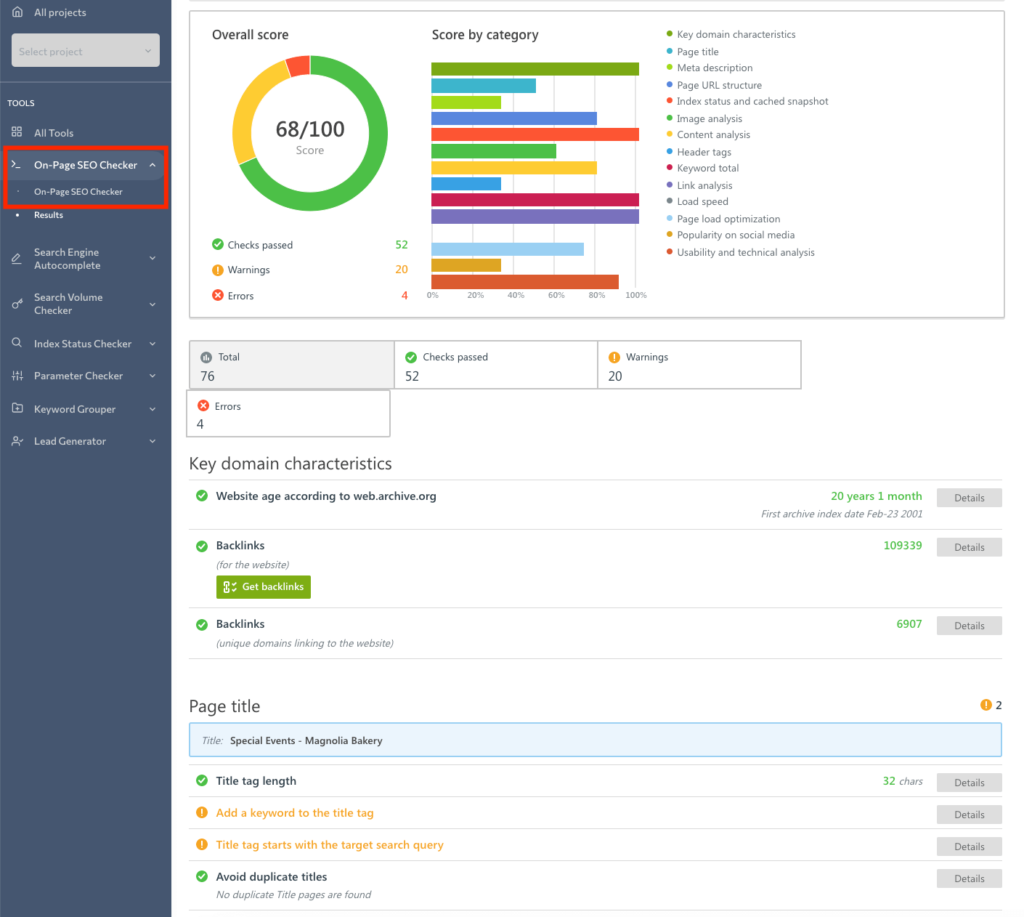
After you’ve done on-page checks, browse through the pages of your competitor’s site simply with your own eyes. Compare the structure and sections of your site and that of your competitor to spot the differences that may affect site ranking and see what you are missing.
Step 8. Find competitive PPC keywords
Even if you don’t intend to run paid ads just yet, learning the PPC keys of your competitors can be very useful to you when developing your marketing strategy. Suppose your competitors are paying for impressions for certain keywords. In that case, they are most likely quite profitable, and you can use them to rank in organic search or, on the contrary, avoid them if the CPC is too high and you are not ready to outbid all competitors.
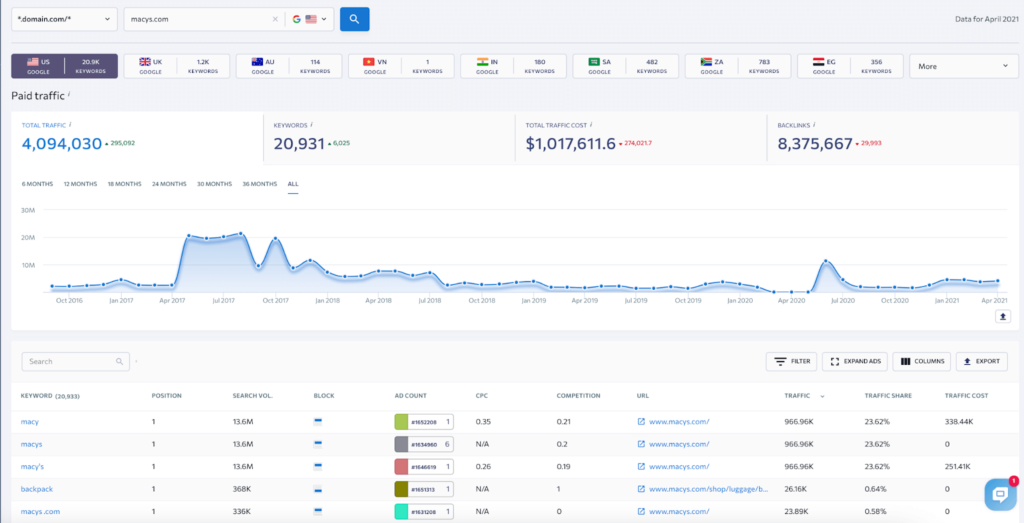
To track the keywords your competitors are using for paid advertising campaigns, go to the Competitive Research tool, enter your competitor’s address, select the Paid Traffic Search section and the Keywords section. There you will see the entire list of keywords for which the company is launching paid ads, as well as their search volume, positions (and their changes), competition rates, URLs of the promoted pages, etc.
Step 9. Analyze PPC ads
Let’s continue with analyzing competitors’ ads. One of the biggest challenges for any company is coming up with ad copy, as it needs to be short and engaging. Companies are testing different ad variations, and sometimes even one changed word can dramatically increase CTR and lead to higher conversions.
Studying your competitors’ advertisements can help you write title tags and descriptions. You will understand which offers work better, what information should be specified in the snippet, and so on.
To thoroughly study your competitors’ ads in Google Ads, you just need to use the Competitive Research tool in SE Ranking. In the Ads History section, you will see the following information:
- Traffic received from ads launched for each keyword and traffic share;
- The number of advertisements that include a certain keyword;
- Search volume;
- Cost per click;
- Full texts of ads for different time periods.
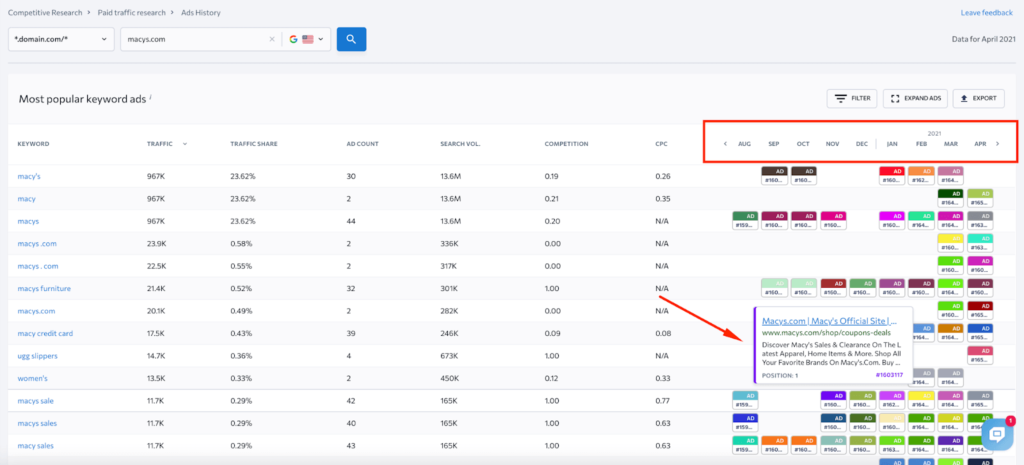
Having studied the ads copy for different months, you can track how the wording has been changed and whether ads that your competitor launches month to month without changing the wording – most likely, these ads are the most profitable for them. Also, pay attention to whether there are keywords that they rarely or no longer run ads for – most likely, such ads do not benefit the company at all.
Summary
Competitor research allows you to legally obtain a lot of information about how your competitors are promoting online. This is important if you are only thinking about starting a business in a specific niche, opening a new direction, or looking to improve your current results.
Thanks to modern tools like SE Ranking, you can study the online presence of your competitors from literally every angle, from the volume and source of the traffic to in-depth analysis of paid ads, right down to their copy and months when they launch such ads. This allows you to plan your own promotional activities better and avoid mistakes based on the competitors’ experience.
Author bio:
 Alina Tytarenko is Outreach Specialist at SE Ranking. She likes sharing her experience in marketing techniques, link building, content marketing, and SEO with readers. You can reach out to her on LinkedIn.
Alina Tytarenko is Outreach Specialist at SE Ranking. She likes sharing her experience in marketing techniques, link building, content marketing, and SEO with readers. You can reach out to her on LinkedIn.
Follow Us